Quick Revision Points AP Economy Part-2
Agriculture and Allied Activities
✦ The percent share of the different segments of land use of the total geographical area in the year 2023-24 of the state: 162.97 lakh hectares. Land utilisation details are shown below –
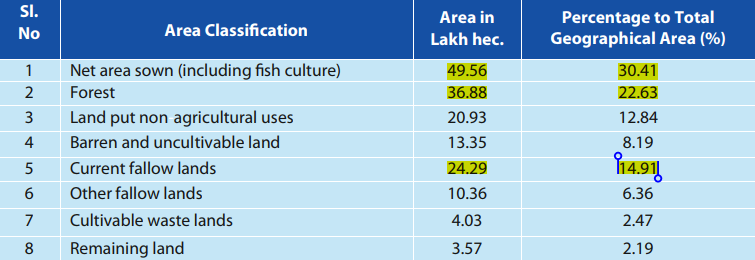
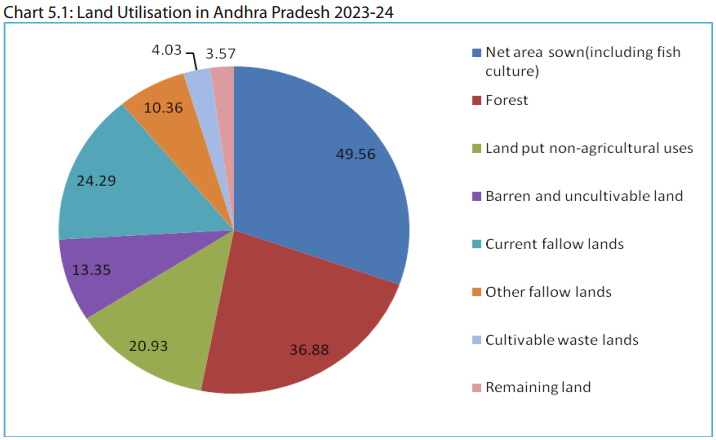
✦ Of the 22 categories of soils adding to the total geographical area of the state, ten types are predominant and together account for over 88% of the area.
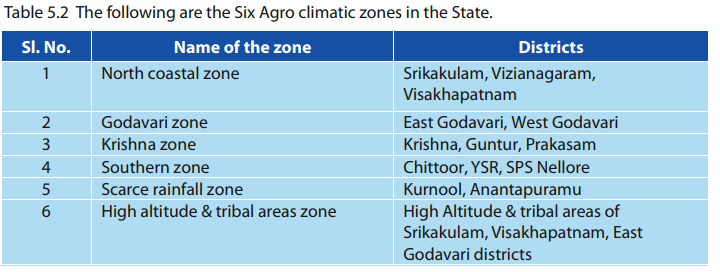
✦ The details of the Six Agro Climatic zones of AP are mentioned in the following table
✦ Data on landholdings is being collected since 1970-71 through a quinquennial Census of landholdings.
✦ Land holdings in the state marginally declined to 0.86 hectares during 2021-22 from 0.94 hectares in 2015-16.
✦ Number of holdings increased from 85.24 lakhs in 2015-16 to 96.90 lakhs in 2021-22.
✦ AP State received rainfall of 487.3 mm during the South West Monsoon period in 2023-24 as against the normal rainfall of 574.7 mm, indicating a deficit of 15.2% (Normal).
✦ AP State received rainfall of 230.9 mm during the North East Monsoon period in 2023-24 as against the normal rainfall of 285.3mm, indicating a deficit of 19.1% (Normal).
✦ During the year 2023-24, the average rainfall received was 802.6 mm as against normal rainfall of 975.3 mm, deficit being 17.7% (Normal).
✦ Area under food grains is 33.32 lakh hectares in 2023-24 as against 36.80 lakh hectares in 2022-23, showing a decrease of 9.45%.
✦ Total production of food grains in 2023-24 is 146.65 lakh tonnes while it was 168.41 lakh tonnes in 2022-23 showing a decrease of 12.92%.
✦ Area under food grains in Kharif 2023-24 is 18.13 lakh hectares, while it was 19.31 lakh hectares in 2022-23 showing a decrease of 6.11%.
✦ Production of food grains in Kharif, 2023-24 is 80.22 lakh tonnes, while it was 85.52 lakh tonnes in 2022-23, showing a decrease of 6.20%.
✦ Area under food grains in Rabi 2023-24 is 15.19 lakh hectares while it was 17.49 lakh hectares in 2022-23 showing a decrease of 13.15%.
✦ Production of food grains in Rabi 2023-24 is 66.43 lakh tonnes while it was 82.89 lakh tonnes in 2022-23 showing a decrease of 19.85%.
✦ Cropping intensity is the ratio of gross cropped area to net cropped area. Cropping intensity for the year 2023-24 is 1.21.
✦ Gross area irrigated in the State decreased to 32.71 lakh hectares in 2023-24 from 36.56 lakh hectares in 2022-23.
✦ Net area irrigated in the state stands at 26.03 lakh hectares in 2023-24.
Key Strategies to make Agriculture Profitable
- Govt. extending financial assistance of Rs.13500/- per farmer family per year (including Rs.6000/-from PMKISAN) under Rythu Bharosa – PMKISAN as an investment support to the farmers started from Rabi, 2019.
- Government of Andhra Pradesh has established 10778 Rythu Bharosa Kendralu (RBKs).
- e-Crop booking is done to create farmer’s database through e-Crop Application. This data base is made mandatory for usage in implementation of Crop Insurance, providing Input subsidy, Sunna Vaddi Panta Runalu and procurement of agriculture produce.
- Govt. is providing exgratia to the farmer families in the event of death by suicides (Agrarian Reasons) / Accidents @ Rs. 7 lakhs per family.
- Andhra Pradesh State Agriculture Mission was established as a policy making & advisory body to address the challenges in delivering quality and timely services to the farming community.
- Polambadi (Farmer Field Schools) aims to empower the farmers to take economically viable decisions by adopting eco-friendly practices of Integrated Crop Management in a scientific manner.
- Supply of 100% Neem Coated Urea to Farmers and certified seed on subsidy.
- Extending crop loans to maximum no. of tenant farmers individually by issuing Crop Cultivator Rights Cards (CCRCs) (or) by forming them into Joint Liability Groups (JLGs).
Rythu Bharosa – PM-KISAN
- Financial assistance to land owning farmers @ Rs. 13,500/- per year per family including Rs. 6000/- from the GoI under PM KISAN in 3 installments –
- Rs. 7500/- in May
- Rs. 4000/- during October
- Rs. 2000/- during January
- Financial assistance is also being provided to SC, ST, BC, Minority category Landless tenant farmers & ROFR cultivators @ Rs. 13,500/- per year per family from AP State budget in 3 installments.
✦ During the year 2023, 120 farmer suicides were reported and paid an Exgratia amount of Rs. 8.40 Cr @ Rs.7.00 Lakhs per farmer family.
✦ Crop Cultivators Right Act 2019 aims to provide all facilities including banking, insurance and other Govt. benefits to tenant farmers without effecting the rights of the owner of the land. The Act came in to Force from 17-08-2019.
✦ Crop Cultivator Rights Cards (CCRC) were issued to tenant farmers on 2nd October, 2019. According to the Act, Crop Cultivator Rights Cards (CCRC) will be issued with the mutual agreement of land owner and cultivar for a period of 11 months, which entitles the tenant farmer to avail bank finance.The CCRC holders are also eligible to get benefits of Government schemes.
✦ During 2023-24, the CCR Cards were issued to 8,31,884 no. of actual cultivators in the state.
✦ Government of AP has implemented the “Sunna Vaddi Panta Runalu (SVPR)” Scheme w.e.f. Kharif, 2019 Interest subsidy for the crop loans upto Rs.1.00 lakh will be transferred directly to the accounts of farmers who have repaid their loans in time (maximum period of one year from date of disbursement of crop loan).
✦ To ensure proper protection of the crops, the State has been implementing Free Crop Insurance Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) and RestructuredWeather based crop insurance (RWBCIS).
✦ AP State has introduced Universal Crop Insurance from Kharif, 2019 onwards. AP farmers are automatically covered under Crop insurance simply based on the e-crop registration for all the notified crops.
✦ Polambadi is a field-oriented training program organized with 30 farmers in a village for a period of 14 weeks, holding one session per week on a fixed day rowed in a week.
✦ India Good Agriculture Practices (IndGAP) certification is a voluntary program that verifies that farms are using safe food practices. Quality Council of India (QCI) developed the IndGAP certification scheme.
✦ In Andhra Pradesh, APSOPCA is the Certifying Body accredited by the QCI to issue Ind.GAP certificate to the producers.
✦ Soil Health Card (SHC) and soil health management schemes were merged under Rashtriya Krishi vikas yojana from 2022-23 and named as Soil Health & Fertility component. The objective of the scheme is to encourage judicious use of fertilizers. STLs analyze the soil samples for 12 parameters.
✦ School Soil Health Programme: Main objective is Children be made aware of the Soil Health so that they become Brand Ambassadors. Trainings will be organized to Teachers & Students.
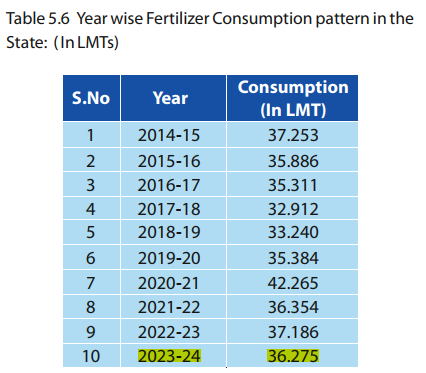
✦ Fertilizer consumption during 2023-24 in terms of product was 36.28 LMT and in term of Nutrient (NPK) was 17.22 LMT.
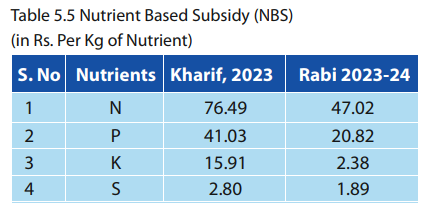
✦ Under the Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Policy, a fixed rate of subsidy (in Rs. Per Kg basis) is announced on nutrients namely Nitrogen (N), Phosphate (P), Potash (K) and Sulphur (S) by the Government on annual basis.
✦ In Andhra Pradesh, there was 266.166 MT (Active Ingredient) reduction of Pesticide consumption during the year 2023-24 (1990.255 MTs of Active Ingredient) compared to the last year’s 2022-23 (2256.421 MTs of Active Ingredient).
✦ IT based Pest and Disease diagnosis and surveillance has been done through Plantix, Gatherix apps and Integrated Call Center (ICC).
✦ Government of India has introduced National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) in 2014-15. Under this mission, Rainfed Area Development (RAD) component is being taken up in convergence with Agri & Allied sectors. Scheme is being implementing in the Rainfed agriculture is more prevelant in (9) districts – Kurnool, Nandyal, Anantapuram, Sri SatyaSai, Kadapa, Annamayya, Chittoor, Tirupathi and Prakasam districts in the State during 2023-24.
✦ Under Yantra Seva Padhakam (2021-22 to 2023- 24),10956 Community Hiring Centres (CHCs) established at RBK and Cluster level.
✦ Agriculture Technology Management Agency – ATMA is a district level autonomous Institution having membership of all key stakeholders involved in agricultural activities. It has the flexibility to receive funds directly. It has the key responsibility of disseminating all technology activities at the district level.
✦ ATMA would be supported by Governing Board (GB) and Management Committee(MC). The Governing Board is a policy making body and the Management Committee would be responsible for planning and executing the day-to-day activities of ATMA.
✦ Andhra Pradesh Integrated Irrigation and AgricultureTransformations Project (APIIATP) is an EAP project taken up by the State of Andhra Pradesh to bring transformation in Irrigated Agriculture. It is a 7-year duration World Bank funded project.
✦ AP Govt. is implementing “Andhra Pradesh Irrigation and Livelihood Improvement Project Phase -II (APILIP –II)” from 21st December 2017 with assistance from Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) with an objective to increase the local productivity, strengthen institutional and marketing capacities. The funding of the project is in the ratio of 84:16 i.e 16% by state govt.
✦ CSS-Formation and Promotion of 10000 Farmers Producers Organizations (FPOs): The objective is to provide holistic and broad-based supportive ecosystem to form new 10,000 FPOs. SFAC, NABARD, NCDC & NAFED are designated as 4 implementing agencies.
✦ Government of Andhra Pradesh has been implementing climate resilient, AP Community managed Natural Farming (APCNF) formerly known as ZBNF in 5300 clusters under PKVY and 5000 clusters under BPKP.
✦ From 615 Gram Panchayaths in 2016, the APCNF programme by March, 2024 scaled up to 4116 Gram Panchayaths, working with farmers and Poorest of Poor families (PoPs), covering all the 658 rural mandals of the state
✦ Indo-German Global Academy for Agroeocology Research and Learning (IGGAARL) has been initiated on 7th July 2022, as a global facility for furthering the research support to Natural Farming.
✦ Rythu Sadhikara Samstha (RySS) received First prize in the category of State government promoting natural farming in large scale during the Jaiwik (organic) India National Awards 2022. Also received National Award for Women’s Development through application of science and technology (STREE award: Dept of Science andTechnology).
✦ Rural Credit Cooperative structure at present is a three-tier structure with the Andhra Pradesh State Cooperative Bank (APCOB) at the APEX level with 18 branches with 13 District Cooperative Central Banks (DCCBs) at the district level with 436 branches located in district headquarters, small towns and semi urban areas and 2042 Primary Agricultural Cooperative Credit Societies at village level.
✦ The main objective of the Primary Agricultural Cooperative Credit Societies (PACS) is to provide credit services to its member farmers at village level. Non-credit services also provided to the members through PACSs.
✦ Andhra Pradesh State Cooperative Bank has disbursed an amount of Rs.199.79 Crores to 20,248 Tenant Farmers towards financial assistance during the year 2023-24 through the PACS.
✦ Centrally Sponsored Scheme“Digitalisation of PACS” is being implemented in Andhra Pradesh to computerise 2037 Primary Agricultural Cooperative Societies at a cost of Rs. 4.00 Lakh per PACS.
✦ AP MARKFED is an apex organization for the Cooperative Marketing Societies (CMS) in the State. Subsequent to interdiction of single window system in the State in 1987, MARKFED offers its services through RBKs, PACSs at the primary level.
✦ AP MARKFED played a key role in creation of Price Stabilization Fund with Rs.3000 Crores to protect farmer interest and MSP for certain crops.
Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana – Remunerative Approaches for Agriculture and Allied Sector Rejuvenation (RKVY – RAFTAAR) is a flagship programme of the Government of India with 60% grant by the Central Government and 40% grants by the State Plan Scheme for construction of Godowns by the PACS.
✦ A.P. State Cooperative Union is an Apex Cooperative institution registered in the field of Cooperative Education and Training and it is functioning with Vijayawada as Headquarters. There are four Cooperative training Centres (CTCs) located at Vijayawada, Rajamundry, Ananthapur and Proddutur in the State working under APSCU.
✦ APSCU is offering 6 months duration certified Diploma course in Co-operative Management and Computer Applications Course.
✦ APSCU is publishing a Cooperative monthly magazine in Telugu titled as “Sahakaara Samaachaaram” for creating awareness about Cooperative Principles.
✦ AP State Cooperative Rural Irrigation Corporation Limited was started in 1981. The Government of Andhra Pradesh has declared APSCRIC Ltd., as Nodal Agency for undertaking all the drilling activities.
✦ Rural Electric Cooperative Societies main objective is to purchase electricity in bulk from nearest DISCOM and distribute it to domestic, industrial and agricultural purpose, functioning under the control of Cooperative Department. There are three RESCOs.
- Kuppam RECS Ltd., Kuppam, Chittoor District
- Anakapalli RECS Ltd., Kasimkota, Anakapalli District
- Cheepurupalli RECS Ltd., Cheepurapalli , Vizianagaram District
✦ AP Cooperative Tribunal (APCT) was constituted under the provisions of Section 75 of AP Cooperative Societies Act1964. It was Chaired by a Judicial Officer not below the rank of District Judge and with two members, not below the rank of Additional Registrar of Cooperation Department.
✦ There is only one Cooperative Tribunal in the State at Vijayawada.
✦ The APCT, Vijayawada also has original jurisdiction over the disputes filed under AP Mutually Aided Cooperative Societies Act, 1995.
✦ APCS Act 1964 provides two different forums for appeal on decisions or orders, awards passed by the Quasi-Judicial Officers of the Department.
✦ There is a separate Audit Wing for Audit in Cooperative Department headed by the Chief Auditor who works under the General superintendence and control of Registrar of Cooperative Societies.
Mahila Dairy Sahakara Sanghalu (MDSS): 912 Mahila Dairy Sahakara Sanghaalu (MDSS) are registered under APCS Act of 1964. Milk is being procured from 1,20,551 Mahila Farmers covering 3408 villages through the 912 registered MDSS and 1086 Mahila Dairy Association Centres.
✦ Total area under Horticulture crops is 45.58 Lakh Acres with a production of 366.53 Lakh MTs (3rdAdvance Estimates,2023-24).
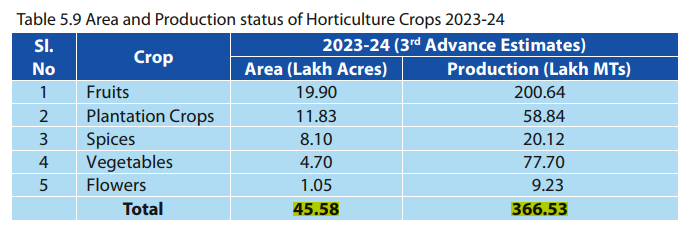
✦ Horticulture sector is one of the major growth engines contributing Rs.54,525 Cr at constant prices & Rs.1,23,533 Cr at current prices to the State GSDP for the year 2022- 23.
✦ Andhra Pradesh is the largest producer of fruits in the country contributing 15.6% of the total country’s fruit production.
| Crop | AP Rank in Productivity |
| Oil palm | 1 |
| Papaya | 1 |
| Lime | 1 |
| Cocoa | 1 |
| Tomato | 1 |
| Chillies | 1 |
| Mango | 2 |
| Sweet Orange | 2 |
| Turmeric | 2 |
✦ During the year 2023-24, Andhra Pradesh State stood at 4th place in the Country in Micro Irrigation (MI) implementation. In top 20, five Districts are from Andhra Pradesh viz., Ananthapuramu, Prakasam, Y.S.R, Sri Sathyasai, and Annamayya.
✦ During the year 2023-24, 1912 crop specific Thotabadi programmes were organized in various horticulture crops.
✦ In AP there are 373 Cold Storages with a capacity of 20.60 Lakh MTs and 247 Ripening Chambers with a capacity of 54315 MTs.
✦ Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme with funding pattern of 60% GoI share & 40% matching State share is being implemented with an objective of promoting holistic growth of horticulture sector.
✦ Rashtriya Krishi VikasYojana (RKVY) is a Centrally Assisted State Plan scheme to implement major activities of Horticulture sector in Non–MIDH Districts. The component integrated vegetable production, which is not covered under MIDH will be covered in the entire State.
✦ Centre of Excellence (CoE) at Pedda Bangarunatham village in Kuppam focuses on the cultivation of flowers and vegetables.
✦ 2nd Centre of Excellence for Vegetables and Spices will be established Gundlapalli Village of Nekarikallu Mandal of Palnadu.
✦ The potential area of Oil Palm is 11.85 Lakh Acres in the State and the area covered as on date is 5.68 Lakh Acres.
✦ Andhra Pradesh Integrated Irrigation and AgricultureTransformation Project (APIIATP) is a world bank funded project aims to enhance agricultural productivity, profitability and climate resilience of poor and marginalized farmers in the state.
✦ Andhra Pradesh Irrigation and Livelihood Improvement Project (APILIP) is a JICA funded project aims to improve value addition of strategic crops in selected districts as pilot programme. It is implemented in 6 districts i.e. Dr. B.R Ambedkar Konaseema, NTR, Palnadu, Chittoor, Tirupati and Annamayya for Value Chain Development of the strategic crops i.e. Coconut, Mango (fresh), Mango (Processing), Chilli andTomato on pilot basis.
✦ Andhra Pradesh stands at 4th position in coconut cultivation with an area of 1.06 lakh Ha and production of 1709 million nuts. Andhra Pradesh stands highest in productivity with 16,000 nuts per Ha.
✦ Andhra Pradesh has emerged as biggest exporter of Banana and was awarded by ICAR-NRC. The first Banana Fruit Train from Tadipatri, AP exported to Middle East countries from Mumbai Port.
✦ AP Govt. is committed to make Rayalaseema Region as Horticulture Hub.
- Total area under Horticulture Plantations in the state is 45.57 Lakh Acres with a production of 366.49 Lakh MTs.
- Out of which, area under Rayalaseema Region is 19.50 Lakh Acres with a production of 189.69 Lakh MTs.
- Rayalaseema Region contributes around 43% of area and 52% production in the entire state.
- Area under Micro Irrigation in Rayalaseema Region is 71% in the State.
| Egg | 1st | 2784.98 lakh eggs |
| Meat | 4th | 10.94 Lakh MTs |
| Milk | 5th | 154.48 Lakh MTs |
✦ Andhra Pradesh is famous for world-renowned livestock breeds such as Ongole and Punganur cattle, Godavari buffaloes, Nellore sheep, and Aseel poultry.
✦ Livestock Census is being conducted across the country periodically since 1919.
✦ 20th Livestock Census (2019) was carried out in 16392 villages and 2985 urban wards across AP covering 1.35 Crores of Households and NonHouseholds
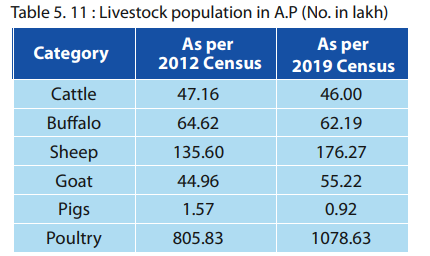
✦ Total Livestock population is 536.76 million in the country showing an increase of 4.6% over Livestock Census, 2012.
✦ Total Livestock population is 34.07 million in AP showing an increase of 15.79% over Livestock Census 2012. AP stands in 6th position in country.
✦ Livestock Population Status (2019 Census): AP has 340.60 lakh livestock and 1078.63 lakh poultry.
✦ Total number of cattle in the country is 193.46 million in 2019 showing an increase of 0.8 % over previous Census.
✦ Total number of cattle in AP is 4.6 million in 2019 showing a decrease of 2.45% over previous Census. AP stands in 14th position in country
✦ Livestock population has grown significantly compared to the 2012 census but there is reduction in the total Cattle and Buffalo Population.
✦ Government established 10606 Rythu Bharosa Kendralu (RBKs) in the State of Andhra Pradesh and permitted to recruit 9844 Animal Husbandry Assistants (AHAs). 6542 AHAs were recruited till date.
✦ Pasu Vignana Badi organized every week to develop skills and knowledge of livestock producers. So far, nearly 4.88 Lakh farmers were participated.
✦ 2902 PasuKissan Credit cards were issued to the farmers by the bankers.
✦ Cheyutha scheme aims to uplift the financial status of the women farmers of BC, SC, ST & Minority communities of 45-56 years age by encouraging livelihood activities like procurement of Milch animals / Sheep / Goat units.
✦ Under Paala Velluva program Milch animals are grounded and supplied to SHG women in convergence with DRDA department.
✦ Under Jeeva Kranthi program Sheep / Goat units are grounded and supplied to SHG women in convergence with DRDA department.
✦ Pasu Bhima Padhakam (Livestock Insurance Scheme) aims to settle the livestock death claims within 15 days after submission of documents. Subsidy for insurance under BPL/SC/ST category will be paid as 40% central share, 40% state share and beneficiary share of 20%. For APL category the share is 25% central, 25% state and 50% beneficiary.
✦ Under A.P Animal Feed Act 2020 & Rules 2021, total 1680 animal feed business operators were issued licenses.
✦ GenericVeterinary Stores (Pasu Aushadha Kendras) aims to reduce the expenses of veterinary medicines and provide affordable and high-quality drugs to livestock farmers and middleincome groups. The plan is to establish 300 Veterinary Generic Drug stores in each Urban Local Body (ULB) and Veterinary Institutions throughout Andhra Pradesh.
✦ Sanchara Pasu Arogya Seva: The Government has proposed to launch the services of “Mobile Ambulatory Veterinary Clinics (MAVCs)” at 340 locations @ 2 for each constituency.
✦ The age-old practise of “Organic Desi Cow Farming” has been rejuvenated by the Government through “Local Breed Conservation Cow Farms (LBCCF)” to make available “the best but the healthy” Milk and Milk products to the consumers at affordable price.
✦ Andhra Pradesh Livestock Development Agency, Guntur supplies Frozen Semen straws and Liquid Nitrogen to all field institutions upto Rythu Seva Kendram level.
✦ Govt. of India has sanctioned National Kamadhenu Breeding Centre to the State of Andhra Pradesh for Southern Region.
✦ A composite livestock farm with Ongole cows and Nellore sheep was started at Chintaladevi in 1986 by the Animal Husbandry Department.
✦ There are 2935 Primary Sheep Breeders Cooperative Societies functioning at village level.
✦ Muddapu Prasad of Srikakulam Dist. received Gopala Ratna Award for the year 2023-24 on 26.11.2023 at Gowhati ( Under Best AI technician category).Awarded – 3rd Prize ( secured 3rd Rank).
✦ Integrated Sample Survey scheme is being conducted in the Andhra Pradesh state since 1976-77 as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme and study the attendant practices of the livestock on 50:50 central and state share basis. The objective of the scheme is to estimate the season wise production of Major Livestock Products i.e., Milk, Egg, Wool and Meat.
✦ SriVenkateswaraVeterinary University,Tirupati stood 31st position in 2023 NIRF rankings among Indian Agricultural Universities. Also received Breed Conservation Award for conserving Punganur & Ongole Breed.
✦ Andhra Pradesh Centre for Advanced Research on Livestock (APCARL), Pulivendula was established with a vision to be a world class centre of excellence for advanced research on Livestock. Its mission is to find solutions to the problems of Livestock.
✦ Andhra Pradesh has 60 lakhs milch animal population of which 58% are buffaloes. The state has got world famous draught breed known as “Ongole” & the poor man’s cattle breed known as “Punganur”.
✦ Andhra Pradesh State Veterinary Council (APSVC) is a statutory body of the A.P. state, to regulate the Veterinary Practice and Education in the state and maintenance of registers of the Veterinary Practitioners.
✦ AP State is contributing about 30% of National fish production for the year 2022-23 and is a major exporter of Shrimp in India with share of 31% in total value of sea food exports of the country.
✦ Fish Production achieved during 2022-23 was 51.06 LMT and for 2023-24 is 51.58 LMT as against annual target of 52.55 LMT.
✦ 51.58 Lakh Tonnes of fish and prawn is produced in the state in 2023-24 with a production growth rate of 1.02%.
✦ HSD oil subsidy to fishing boats enhanced from Rs.6.03 to Rs.9.00 per litre to benefit 20812 boats. All the registered Mechanized and Motorized crafts are made eligible to avail HSD oil subsidy irrespective of registration date.
✦ Ex-gratia to deceased fishermen (who died while fishing) family enhanced to Rs.10.00 lakhs from Rs.5.00 Lakhs.
✦ Government has taken up construction of 10 Fishing Harbours and 6 Fish Landing Centres.
✦ As per Coastal Aquaculture Authority Act and Rules, land within a distance of two kilometres from High Tide Line (HTL) of seas, rivers, creeks and back waters comes under the purview of Coastal Aquaculture Authority (CAA).
✦ A.P State Aquaculture Development Authority (APSADA) is constituted under the Chairmanship of Hon’ble Chief Minister which aims to promote unorganized aquaculture sector in the state to a well organized aquaculture industry.
✦ AP Fish Feed (Quality Control) Act, 2020 was enacted to ensure the production and supply of quality Fish & Shrimp feed.
✦ AP Aquaculture Seed (Quality Control) (Amendment) Act 2020 has been enacted to ensure production & supply of quality Aquaculture seed.
✦ AP Fisheries University Act 2020 was enacted for the establishment of the Fisheries University in West Godavari district.
✦ Fishing ban on marine fishing for 61 day will be observed from 15th April to 14th June every year with an objective of conserving the fishery wealth and to sustain the fish production from marine waters. From 2024-25, the Government enhanced the relief to Rs. 20,000/– from Rs.10,000/- per family.
✦ Supply of power @Rs.1.50/unit to all eligible aqua farms located in both aqua and non aqua zones.
✦ Indian State Forest Report 2021: Andhra Pradesh state forest covers an area of 38060.39 Sq. Kms, which amount to 23.35% of the total geographical area.
- Very Dense Forest is 1994.28 Sq. Kms
- Moderate Dense Forest is 13928.75 Sq. Kms
- Open Forest is 13861.27 Sq.Kms
- Scrub Forest is 8276.09 Kms
✦ State Forest Development Agency (SFDA) is a society registered as a federation of FDAs in the State. 22 FDAs have been sanctioned by Government of India for implementing National Afforestation Programme (NAP), which is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS).
✦ GOI has merged the National Afforestation Programme (NAP) and National Mission for a Green India (GIM) into a single scheme from 2021-22 onwards.
✦ 7 Temple Eco-parks are being developed in the state to create awareness on various environmental issues.
Dr.Y.S. Rajasekhara Reddy Smruthi Vanam project was developed in an extent of 22.80 Ha in Nallakalva Village of Atmakur Mandal.
✦ Income from forestry sector in the state during 2023- 24 (up to March, 2024) is Rs.32.81 crore.
✦ The notified forest area of A.P. is 37,221.11 Sq.km, which is 22.84% of geographical area. Forest under Protected Area Network is 8139.88 Sq.km, which is 21.87% of notified forest area.
✦ Andhra Pradesh has one Tiger Reserve (FDPT Srisailam Circle), one Elephant Reserve (Koundinya Sanctuary and Rayala Elephant Reserve, Anatapuramu Circle), one Biosphere Reserve (Seshachalam – Spread in Tirupathi and Kurnool Circles), 3 National Parks and 13 Wildlife Sanctuaries in the state.
✦ AP harbours some of the rare and endangered flora like Petrocarpussantalinus (Red Sanders), Cycasbeddomi , Shoreatambaggia , Syziziumalternifolium, Terminaliapallida etc.
✦ AP has the Second Largest Mangrove eco-system in the country (Godavari and Krishna Estuaries.)
✦ Two Zoological parks in the state namely Indira Gandhi Zoological Park at Visakhapatnam and Sri Venkateswara Zoological Park at Tirupati.
✦ There is One deer park in the state i.e., Kandaleru Deer Park at Kandaleru Dam, Nellore.
✦ Nagarjunasagar Srisailam Tiger Reserve with an area of 3727.50 sq.kms. is one of the largest conservation landscapes in the country.This is one of the country’s rich biodiversity hot spots. The primitive tribal group ‘Chenchus’ have been involved in the management of NSTR.
✦ Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve with an area of 4755.997 Sq. km. is located in Seshachalam Hill-ranges of Eastern Ghats.
✦ Olive Ridley Turtles started coming to Andhra Pradesh for the past (10) years along the coasts of Srikakulam, Vizianagaram, Visakhapatnam, East Godavari, Krishna, Guntur, Prakasam, Nellore. Start nesting during the month of December up to May for a period of 5-6 months.
✦ Red Sanders Protection Scheme is meant for protection of Red Sanders trees in Seshachalam, Veligonda, Lankamala, Nallamala and Talakona Hill Ranges of Andhra Pradesh distributed in the districts of Annamayya, Kadapa, Nandyal, Chittoor, Nellore, Tirupati and Prakasam over an area of 5300.97 Sq.Km.
✦ Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management & Planning Authority (CAMPA): Government of India, Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has constituted an authority known as CAMPA for conservation, protection, regeneration and management of existing natural forests and wildlife.
✦ AP State Biodiversity Board aims to achieve zero loss of biodiversity and ecosystems services by 2030.
✦ APSBB has started City Biodiversity Index Project in 4 Major Cities of Andhra Pradesh by e- Tender process for i.e Visakhapatnam, Vijaywada, Kadapa and Tirupati.
✦ MERI LiFE web portal is an initiative by the Indian government to promote environmentally conscious lifestyles, particularly among young people. It’s connected to the broader Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) movement, which aims to encourage individuals to adopt sustainable practices in their daily lives.
✦ A.P. Forest Development Corporation Ltd. has developed Eco Tourism Centers at Muthayapalem near Suryalanka Beach and Ananthagiri near Araku.
✦ National Green Corps is a major initiative of MOEF&CC, GOI for creating environmental awareness among school children launched in 2001-02. To implement this programme Andhra Pradesh National Green Corps was formed as nodal agency during 2002-03.
✦ AP Pollution Control Board was established in the year 1976 by the Government of Andhra Pradesh under the provisions of Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
✦ Waste to Energy (WtE) plants were established at Visakhapatnam – 15 MWH and Guntur – 20 MWH catering the needs of ULBs for effective disposal of Municipal Solid Waste.
✦ AP Pollution Control Board has installed and commissioned roof top solar power systems at Vijayawada, Visakhapatnam and Kakinada office buildings towards achieving Zero Net Energy.
✦ Sericulture comprises cultivation of food plants such as mulberry, castor, terminalia etc., and rearing of silkworms followed by silk reelingTwisting, Warping, Weaving etc.
✦ Sericulture is predominant in Sri SatyaSai, Chittoor, Anantapuramu and also in Annamayya, Kakinada, Kurnool, Prakasam and Kadapa districts.
✦ AP produces Mulberry and Tasar Silks.
✦ Rearing of Eri silkworms for production of spun silk has also picked up recently and is called as Ahimsa Silk.
✦ AP stands at 2nd position in India after Karnataka in practicing Mulberry sericulture.
✦ AP is the 2nd largest producer of Raw silk in the Country after Karnataka.
✦ AP is the 2nd State next to Karnataka in implementing Sericulture e-marketing in the country.
✦ AP was awarded with ‘Best Bivoltine Practicing State in India’ by the Ministry of Textiles.
✦ In Andhra Pradesh, the Silk Samagra scheme (Central sector scheme) is being implemented with the assistance from Central Silk Board with an aim of technology development and absorption, quality up-gradation, improvement of investment potential productivity, employment generation especially to women, SC/ ST and below poverty line farmers.
✦ Pattu Badi programmes are being organized by the department under RKVY to motivate new farmers and for productivity improvement.
✦ Silk fabric producing clusters in Andhra Pradesh at Dharmavaram, Mudireddipalli (Anantapuramu dist.), Uppada, Peddapuram (E.Godavari dist.), and Neerugattuvaripalli (Chittoor dist.).
✦ Andhra Pradesh State Sericulture Research and Development Institute (APSSRDI), Hindupur in Ananthapuramu district has focused at a significant mandate of developing silkworm breeds / hybrids.
✦ Agricultural Marketing: There are 1052 godowns with capacity to store 9,65,492 MTs are existing in the state, of which 612 godowns with a storage capacity of 5,52,900 MTs are underutilization.
✦ During 2023-24 under e-NAM, 2,047 farmers registered, 225 Traders & 18 Commission agents and 113 FPOs registered in the state. 12.19 Lakh MT quantity with a trade value of Rs.10,211.06 Crores traded in e-NAM.
✦ Rythu Bazars were established in the year 1999 with an objective of direct sale of vegetables by the farmers without intermediaries.
Source: AP Socio Economic Survey



